Stockpiles
A stockpile is a temporary destination to store the mined material.
You can set up four types of stockpiles in Strategy:
Each type of stockpile has been designed to correspond to different mining scenarios. All stockpiles that have been added to a setup will be completely depleted by the end of a schedule, the same as pits.
Process stockpiles
Process stockpiles are a simple way of adding stockpiling behaviour to a Strategy project. When enabled, each process is given its own attached stockpile that feeds only that process.
To turn on process stockpiles, select Allow process stockpiles checkbox in the ![]() Economic Model >
Economic Model > ![]() Configuration subtab.
Configuration subtab.
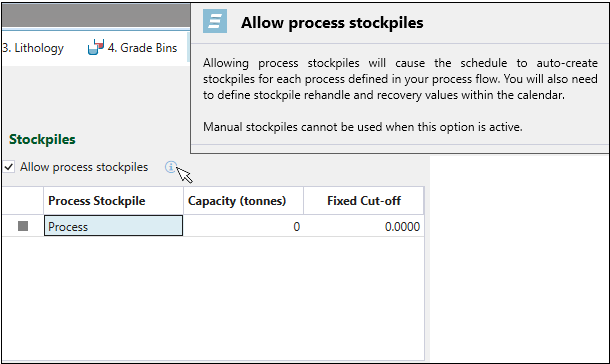
Note: If process stockpiles are enabled, they will be added for all processes in your setup.
Process stockpiles can be set with maximum capacities, and can also have their cut-off grade set to a fixed value by the user. See Configuration for more information.
Process stockpiles allow you to:
-
Increase project net present value (NPV) by delaying the extraction of low grade material in the schedule.
-
Keep a process up to capacity in periods when low ore is coming from the pit.
-
Blend ore mined directly from the pit with reclaims from the stockpile to meet grade tolerances.
-
Fully utilise mining capacity even when all mills or processes are full.
Note: Without this function, mining would have to cease, as there is nowhere to send any ore that might be mined. While generally it is ideal to mine waste as late as possible, it is sometimes advantageous to mine waste in advance to expose ore in later periods. If some of this waste is dependent on a small amount of ore above being removed first, then this could only occur if there are stockpiles to store that excess ore when the mill is full.
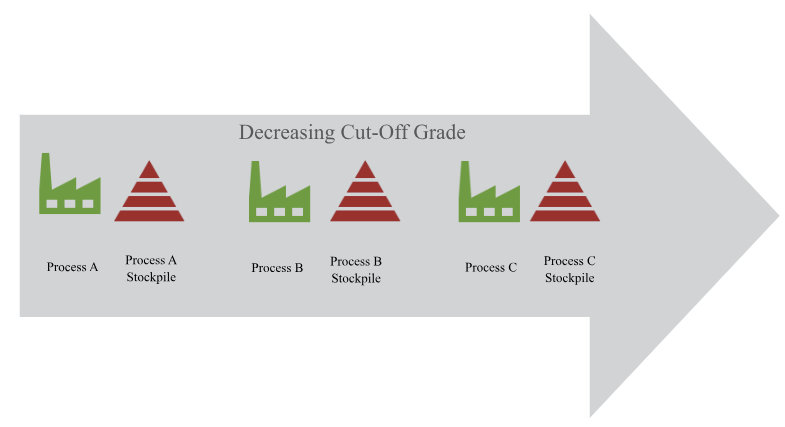
Strategy will choose cut-off grades for each process stockpile that is below the cut-off of the process it is attached to, but above the process with the next highest cut-off. This will result in the following cut-off grade regime:
Overflow stockpiles
Overflow stockpiles act as simple stockpiles that accept all material above the capacity of the process in a given period, which can later be reclaimed to meet capacity in periods of low ore mining.
Important! Overflow stockpiles do not have their own cut-off grade (they share the cut-off of their assigned process) and hence cannot be used for blending purposes or to help keep head grades within tolerances.
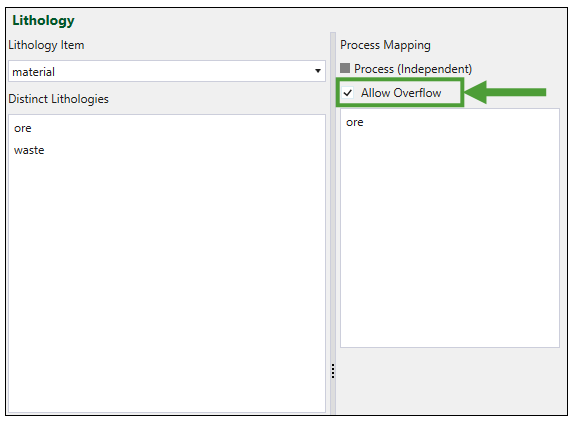
You can turn a process stockpile, which has been assigned to a particular process, into an overflow stockpile. To do so, select the Allow Overflow checkbox for each process in the ![]() Lithology tab.
Lithology tab.
As with process stockpiles, overflow stockpiles can have maximum capacities set in the ![]() Economic Model >
Economic Model > ![]() Configuration subtab.
Configuration subtab.
Overflow stockpiles allow you to:
-
Keep a process up to capacity in periods of low ore coming from the pit.
-
Fully utilise mining capacity even when all mills or processes are full.
Note: Without this function, mining would have to cease, as there is nowhere to send any ore that might be mined. While generally it is ideal to mine waste as late as possible, it is sometimes advantageous to mine waste in advance to expose ore in later periods. If some of this waste is dependent on a small amount of ore above being removed first, then this could only occur if there are stockpiles to store that excess ore when the mill is full.
While process stockpiles also offer these advantages, due to having a cut-off grade below the process, it is possible that high grade ore might prevent the mining of underlying waste, since there is nowhere to send the ore. Overflow stockpiles eliminate this problem.
Manual stockpiles
Manual stockpiles are the most flexible form of stockpiling in Strategy. Thanks to the following properties, they provide the functionalities which cannot be found in other stockpile types. Manual stockpiles can be characterised by:
-
Being only fed by pits linked to them in the Flowchart.
-
Their ability to feed multiple processes, but only those processes that are linked to them in the Flowchart.
-
The possibility to limit them to the material from particular domains or lithologies set as block model attributes.
-
Their ability to restrict ore based on upper and lower grade bounds for multiple grade elements.
You can add manual stockpiles to your setup directly in the flowchart and define their settings in the ![]() Configuration subtab (see Process Flow and Configuration for more information). Similarly to other stockpile types, you can also specify a maximum capacity.
Configuration subtab (see Process Flow and Configuration for more information). Similarly to other stockpile types, you can also specify a maximum capacity.
Initial stockpiles
Initial stockpiles are used to represent any material that exists on a stockpile prior to the start date of the schedule. They provide an easy way of supplying a set tonnage and grade of material that can be reclaimed by processes linked in the flowchart. Unlike other types of stockpiles, initial stockpiles cannot accept new material during the schedule. You can add initial stockpiles to your setup in the flowchart. See Process Flow for more information.
